
To hedge this risk, Company A enters into a forward contract to sell $200,000 CAD at a fixed rate of $0.75 USD per Canadian dollar. Companies with floating-rate loans can use interest rate swaps to convert variable payments into fixed ones. This eliminates uncertainty about future interest expenses and makes budgeting more predictable.
- A negative cash flow hedge reserve balance can indicate issues with hedge effectiveness that may impact financial reporting.
- Similarly, an exporter selling products in euros might hedge against currency movements that could reduce dollar revenues.
- If the actual pool price is $70, the producer gets $70 but has to rebate $20 to the retailer, the “difference” between the strike price and the pool price.
- This initial journal entry sets up the hedge and records the fair value of the derivative asset.
- Advantages of equity financing over debt financing include that it boosts growth without burdening cash flow or risking personal assets.
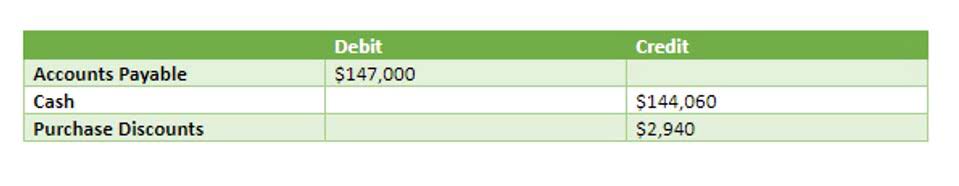
- On the date of sale, BC Corp. prepares the journal entry for the foreign-currency denominated sale, assuming a periodic inventory system and the purchase of the option.
Tax Considerations
Libor declined on July 15, 2016 and caused an increase in the fair value of the debt. In this scenario, Entity A has not benefited from the execution of the swap, since the interest rate has increased. In this scenario, Entity A has benefited from the execution of the swap, since the interest rate has declined. Get a brief on the top business stories of the week, plus CEO interviews, market updates, tech and money news that matters to you. As a more concrete example, let’s say that your company will need to buy 1000 tons of copper next year, which sells for $4,585 per ton as of this writing. So you expect an expense of $4,585,000 for your copper needs, and you use this figure when planning your budget.
- This type of hedge is commonly used to work against risks arising from changes in the fair market value of liabilities, assets, or other commitments.
- ExxonMobil has been able to maintain high credit ratings, even in times of low oil prices because of their future-forward hedging strategies.
- When you’re out driving your car, there is a risk that you could get into an accident and cause costly damage to other drivers’ property.
- Both fair value and cash flow hedges are invaluable in managing financial uncertainty.
- Differences in the respective exceptions are nuanced, but at a high level each is intended to provide relief to requirements that would otherwise cause hedging relationships to be modified or otherwise affected.
What’s the core difference between a cash flow hedge and a fair value hedge?

In this example, the change in the jet fuel swap’s fair value is recorded in Other Comprehensive Income on the balance sheet. This is the hallmark of a cash flow hedge – gains/losses on the derivative are recorded in equity, rather than net income. To qualify as a hedging instrument, a foreign currency hedge must be a contract with a party external to the reporting entity, such as a forward exchange cash flow hedge vs fair value hedge contract or a futures contract. A hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation is the third type of hedging relationship.
- By understanding the distinctions between these tools, companies can adopt the appropriate strategy to address their specific risks.
- Both IFRS 9 and US GAAP5 provide guidance to help support the transition from benchmark interest rates that are being discontinued by providing relief to specific hedge accounting requirements.
- Cash flow hedge gains/losses affect other comprehensive income first while fair value hedge gains/losses directly hit earnings.
- The net effect on earnings for each period is the difference between the gain or loss from the change in the spot rate and the gain or loss from the change in the forward rate.
- According to the International Accounting Standards (IAS) and IFRS 9, such hedges can qualify for hedge accounting if the changes in the cash flow can potentially affect the income statement.
- Imagine a company owns an asset valued at $50,000, but market conditions threaten to reduce its worth to $40,000.
Demystifying Hedge Accounting: Navigating Cash Flow and Fair Value Hedges

This ASU does not change the “highly effective” threshold in hedge accounting that this article discussed earlier. It neither changes the benchmark interest rate concept for fixed-rate financial instruments classified as fair value hedges even though it eliminates it for variable-rate financial instruments classified as cash flow hedges. Furthermore, this ASU not only retains both the shortcut method and critical-terms-match method, but also provides additional relief for entities applying those methods. Finally, this ASU adds new disclosure requirements, for example, entities must disclose the carrying amounts and cumulative basis adjustments of items designated and qualifying as hedged items in fair value hedges. The $4,055 gain on the forward contract is the Opening Entry change in the fair value of the contract during the period, and is recognized in other comprehensive income. The one-month amortization of the premium on the forward contract ($100) is reclassified out of other comprehensive income into earnings in the same line of the income statement as the foreign currency exchange loss on the payable.
One of the main challenges of fair value hedges is that they can create significant fluctuations in your balance sheet, as the carrying value of the hedged item changes with the market conditions. This can affect your financial ratios, solvency, and leverage, and may have implications for your credit rating, debt covenants, or regulatory requirements. Another challenge of fair value hedges is that they can only be used to net sales hedge recognized assets or liabilities, or firm commitments, that are exposed to a specific risk. This limits your ability to hedge anticipated transactions that are not yet contracted, or to hedge multiple risks that affect the same item.

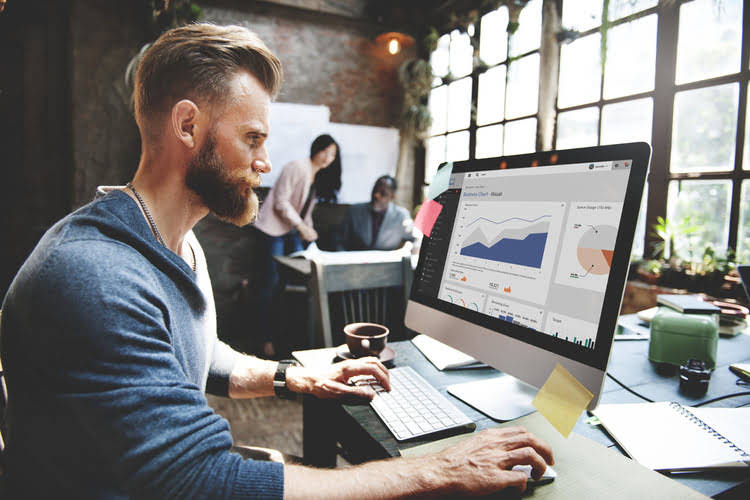
Navigating it starts with understanding the differences between cash flow hedges vs. fair value hedges, which is also key to managing risk. Some common financial instruments used for hedging include futures contracts and options. Futures contracts can be used to lock in the value of an asset, such as a raw material inventory, at a certain price. For example, Company A, a manufacturing corporation, used a futures contract to hedge against a potential decrease in the value of its raw material inventory. Fair value hedges involve hedging the exposure to a specific risk, such as a change in the fair value of a financial instrument. Cash flow hedges, on the other hand, involve hedging a future cash flow, such as a future payment or receipt.
